업데이트 12/12: Olmo 3.1 발표
Olmo 3 모델 흐름이 처음 공개된 이후, 저희 팀은 모델의 추론 및 명령 추종 기능을 개선하는 데 주력해 왔습니다. 그 결과, 현재까지 가장 뛰어난 성능을 자랑하는 두 개의 새로운 32B 체크포인트를 완성했습니다.
Olmo 3.1 Think 32B 는 기존의 최상의 강화 학습(RL) 실행 결과를 훨씬 더 긴 훈련 일정으로 확장한 결과물입니다.
Olmo 3.1 Instruct 32B 는 Olmo 3 Instruct 7B의 기본 레시피를 훨씬 더 큰 모델에 적용한 것으로, 사용자들이 요청해왔던 부분을 채워줍니다.
Olmo 3 출시 이후, 저희는 Olmo 3 32B Think의 강화 학습을 재개하여 Dolci-Think-RL 데이터셋을 기반으로 224개의 GPU에서 21일 동안 추가 에포크를 적용하여 학습을 진행했습니다. 그 결과, 수학, 추론, 명령 추종 벤치마크에서 상당한 성능 향상을 보여주는 Olmo 3.1 32B Think가 탄생했습니다. AIME에서 5점 이상, ZebraLogic에서 4점 이상, IFEval에서 4점 이상, IFBench에서 20점 이상 향상되었으며, 코딩 및 복잡한 다단계 작업에서도 더욱 강력한 성능을 보였습니다.
https://allenai.org/blog/olmo3
– This notebook is purposefully minimal and focuses on the code to re-implement Olmo 3 7B and 32 models from Allen AI in pure PyTorch without relying on other external LLM libraries; Olmo 3 is interesting because it is currently the leading fully open-source model
– For more information, see the official [Olmo 3 announcement](https://allenai.org/blog/olmo3) and model cards:
– [Olmo-3-1025-7B](https://huggingface.co/allenai/Olmo-3-1025-7B) (base model)
– [Olmo-3-7B-Instruct](https://huggingface.co/allenai/Olmo-3-7B-Instruct)
– [Olmo-3-7B-Think](https://huggingface.co/allenai/Olmo-3-7B-Think)
– Note that there are also 32B versions, which are not listed above for brevity; you can find a complete list [here](https://huggingface.co/collections/allenai/olmo-3-post-training)
– Below is a side-by-side comparison with Qwen3 8B as a reference model; if you are interested in the Qwen3 0.6B standalone notebook, you can find it [here](../11_qwen3)
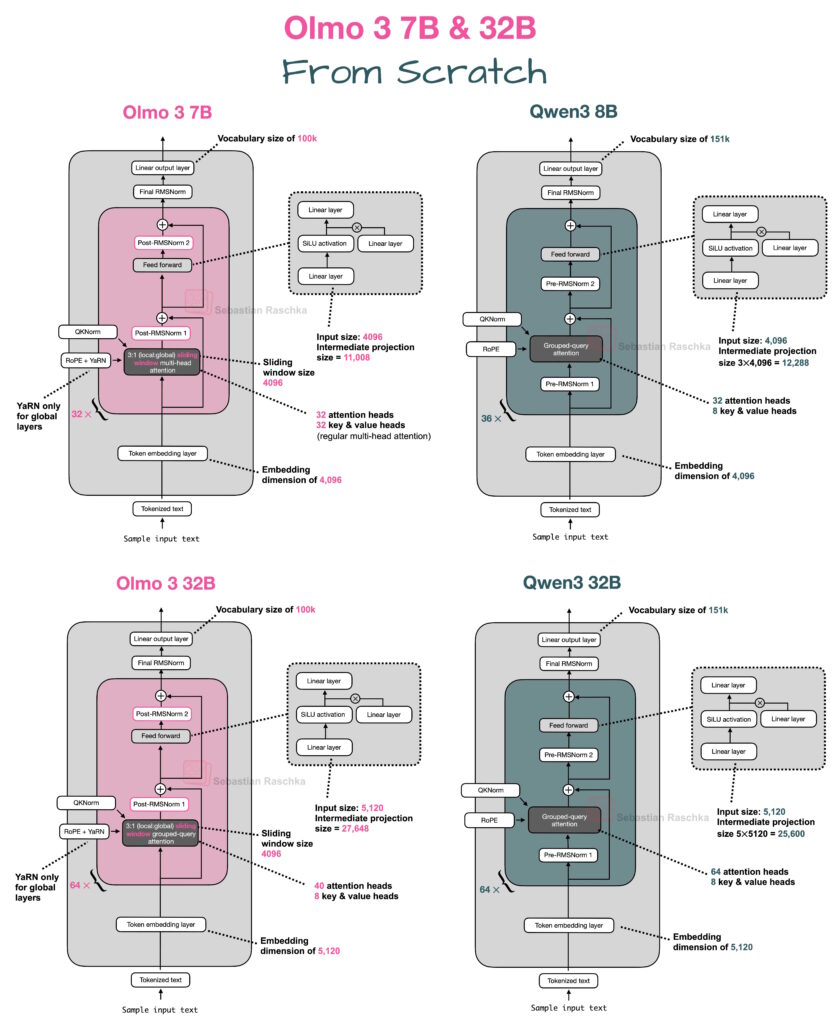
– About the code:
– all code is my own code, mapping the Olmo 3 architecture onto the model code implemented in my [Build A Large Language Model (From Scratch)](http://mng.bz/orYv) book; the code is released under a permissive open-source Apache 2.0 license (see [LICENSE.txt](https://github.com/rasbt/LLMs-from-scratch/blob/main/LICENSE.txt))
# pip install -r https://raw.githubusercontent.com/rasbt/LLMs-from-scratch/refs/heads/main/ch05/07_gpt_to_llama/requirements-extra.txtfrom importlib.metadata import version
pkgs = [
"huggingface_hub", # to download pretrained weights
"tokenizers", # to implement the tokenizer
"torch", # to implement the model
]
for p in pkgs:
print(f"{p} version: {version(p)}") huggingface_hub version: 0.35.0
tokenizers version: 0.22.1
torch version: 2.9.1+cu130
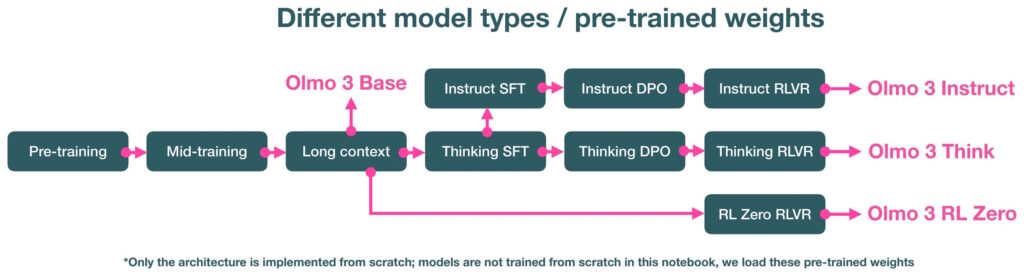
– Note that there are three model types, and each of the four model types comes in a 7B and 32B size:
1. Base (Olmo-3-1025-7B and Olmo-3-1125-32B)
2. Instruct (Olmo-3-7B/32B-Think)
3. Reasoning (Olmo-3-32B/7B-Think)
# Select which model to use # USE_MODEL = "Olmo-3-1025-7B" # USE_MODEL = "Olmo-3-1125-32B" USE_MODEL = "Olmo-3-7B-Instruct" # USE_MODEL = "Olmo-3-32B-Instruct" # USE_MODEL = "Olmo-3-7B-Think" # USE_MODEL = "Olmo-3-32B-Think" # USE_MODEL = "Olmo-3-7B-RLZero-IF"
– In addition to the checkpoints listed above, you can also use the intermediate checkpoints listed [here](https://huggingface.co/collections/allenai/olmo-3-post-training); since they all have the same architecture, they are all compatible with this notebook
1. Architecture code
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
class FeedForward(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, cfg):
super().__init__()
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(cfg["emb_dim"], cfg["hidden_dim"], dtype=cfg["dtype"], bias=False)
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(cfg["emb_dim"], cfg["hidden_dim"], dtype=cfg["dtype"], bias=False)
self.fc3 = nn.Linear(cfg["hidden_dim"], cfg["emb_dim"], dtype=cfg["dtype"], bias=False)
def forward(self, x):
x_fc1 = self.fc1(x)
x_fc2 = self.fc2(x)
x = nn.functional.silu(x_fc1) * x_fc2
return self.fc3(x)
class RMSNorm(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, emb_dim, eps=1e-6):
super().__init__()
self.eps = eps
self.weight = nn.Parameter(torch.ones(emb_dim))
def forward(self, x):
input_dtype = x.dtype
x_f = x.float()
var = x_f.pow(2).mean(dim=-1, keepdim=True)
x_norm = x_f * torch.rsqrt(var + self.eps)
return (self.weight * x_norm).to(input_dtype)
def compute_rope_params(head_dim, theta_base=10_000, context_length=4096, attention_factor=1.0, rope_type="default", rope_factor=1.0, rope_orig_max=8192, dtype=torch.float32):
assert head_dim % 2 == 0, "Embedding dimension must be even"
# Compute the inverse frequencies
inv_freq = 1.0 / (
theta_base ** (
torch.arange(0, head_dim, 2, dtype=dtype)[: head_dim // 2].float()
/ head_dim
)
)
# Generate position indices
positions = torch.arange(context_length, dtype=dtype)
# Optional YaRN scaling
if rope_type == "yarn":
positions = positions / rope_factor
positions = torch.clamp(positions, max=rope_orig_max - 1)
# Compute the base angles (shape: [context_length, head_dim // 2])
angles = positions.unsqueeze(1) * inv_freq.unsqueeze(0)
# Expand to full head_dim (shape: [context_length, head_dim])
angles = torch.cat([angles, angles], dim=1)
# Precompute sine and cosine
cos = torch.cos(angles) * attention_factor
sin = torch.sin(angles) * attention_factor
return cos, sin
def apply_rope(x, cos, sin):
# x: (batch_size, num_heads, seq_len, head_dim)
batch_size, num_heads, seq_len, head_dim = x.shape
assert head_dim % 2 == 0, "Head dimension must be even"
# Split x into first half and second half
x1 = x[..., : head_dim // 2] # First half
x2 = x[..., head_dim // 2 :] # Second half
# Adjust sin and cos shapes
cos = cos[:seq_len, :].unsqueeze(0).unsqueeze(0) # Shape: (1, 1, seq_len, head_dim)
sin = sin[:seq_len, :].unsqueeze(0).unsqueeze(0)
# Apply the rotary transformation
rotated = torch.cat((-x2, x1), dim=-1)
x_rotated = (x * cos) + (rotated * sin)
# It's ok to use lower-precision after applying cos and sin rotation
return x_rotated.to(dtype=x.dtype)
class GroupedQueryAttention(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, d_in, num_heads, num_kv_groups, head_dim, attention_bias=False, dtype=None, sliding_window=None, attn_type="full_attention"):
super().__init__()
assert num_heads % num_kv_groups == 0, "num_heads must be divisible by num_kv_groups"
self.num_heads = num_heads
self.num_kv_groups = num_kv_groups
self.group_size = num_heads // num_kv_groups
self.head_dim = head_dim
self.d_out = num_heads * head_dim
self.attn_type = attn_type
self.sliding_window = sliding_window if attn_type == "sliding_attention" else None
# Projections
self.W_query = nn.Linear(d_in, self.d_out, bias=attention_bias, dtype=dtype)
self.W_key = nn.Linear(d_in, num_kv_groups * head_dim, bias=attention_bias, dtype=dtype)
self.W_value = nn.Linear(d_in, num_kv_groups * head_dim, bias=attention_bias, dtype=dtype)
self.out_proj = nn.Linear(self.d_out, d_in, bias=attention_bias, dtype=dtype)
# Olmo3-style RMSNorm over the flattened projections
self.q_norm = RMSNorm(self.d_out)
self.k_norm = RMSNorm(num_kv_groups * head_dim)
def forward(self, x, mask, cos, sin):
b, num_tokens, _ = x.shape
# Apply projections
queries = self.W_query(x) # (b, num_tokens, num_heads * head_dim)
keys = self.W_key(x) # (b, num_tokens, num_kv_groups * head_dim)
values = self.W_value(x) # (b, num_tokens, num_kv_groups * head_dim)
# Normalize q and k
queries = self.q_norm(queries)
keys = self.k_norm(keys)
# Reshape to (b, heads, seq, head_dim)
queries = queries.view(b, num_tokens, self.num_heads, self.head_dim).transpose(1, 2)
keys = keys.view(b, num_tokens, self.num_kv_groups, self.head_dim).transpose(1, 2)
values = values.view(b, num_tokens, self.num_kv_groups, self.head_dim).transpose(1, 2)
# Apply RoPE
queries = apply_rope(queries, cos, sin)
keys = apply_rope(keys, cos, sin)
# Expand KV groups to full head count
if self.group_size > 1:
keys = keys.repeat_interleave(self.group_size, dim=1)
values = values.repeat_interleave(self.group_size, dim=1)
# Scaling before the matmul seems to be a bit more stable for Olmo
scale = self.head_dim ** -0.5 # Python float
queries = queries * scale
# Attention
attn_scores = queries @ keys.transpose(2, 3)
if mask is not None:
attn_scores = attn_scores.masked_fill(mask, -torch.inf)
attn_weights = torch.softmax(attn_scores, dim=-1)
context = (attn_weights @ values).transpose(1, 2).reshape(b, num_tokens, self.d_out)
return self.out_proj(context)
class TransformerBlock(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, cfg, attn_type):
super().__init__()
self.attn_type = attn_type
self.att = GroupedQueryAttention(
d_in=cfg["emb_dim"],
num_heads=cfg["n_heads"],
num_kv_groups=cfg["n_kv_heads"],
head_dim=cfg["head_dim"],
attention_bias=cfg["attention_bias"],
dtype=cfg["dtype"],
sliding_window=cfg["sliding_window"],
attn_type=attn_type,
)
self.ff = FeedForward(cfg)
self.post_attention_layernorm = RMSNorm(cfg["emb_dim"], eps=cfg["rms_norm_eps"])
self.post_feedforward_layernorm = RMSNorm(cfg["emb_dim"], eps=cfg["rms_norm_eps"])
def forward(self, x, mask_global, mask_local, cos, sin):
attn_mask = mask_local if self.attn_type == "sliding_attention" else mask_global
shortcut = x
x_attn = self.att(x, attn_mask, cos, sin)
x_attn = self.post_attention_layernorm(x_attn)
x = shortcut + x_attn
shortcut = x
x_ffn = self.ff(x)
x_ffn = self.post_feedforward_layernorm(x_ffn)
x = shortcut + x_ffn
return x
class Olmo3Model(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, cfg):
super().__init__()
assert cfg["layer_types"] is not None and len(cfg["layer_types"]) == cfg["n_layers"]
self.tok_emb = nn.Embedding(cfg["vocab_size"], cfg["emb_dim"], dtype=cfg["dtype"])
self.blocks = nn.ModuleList([TransformerBlock(cfg, attn_type) for attn_type in cfg["layer_types"]])
self.final_norm = RMSNorm(cfg["emb_dim"], eps=cfg["rms_norm_eps"])
self.out_head = nn.Linear(cfg["emb_dim"], cfg["vocab_size"], bias=False, dtype=cfg["dtype"])
self.cfg = cfg
cos, sin = compute_rope_params(
head_dim=cfg["head_dim"],
context_length=cfg["context_length"],
theta_base=cfg["rope_base"],
attention_factor=cfg["rope_attention_factor"],
rope_type=cfg["rope_type"],
rope_factor=cfg["rope_factor"],
rope_orig_max=cfg["rope_orig_max"],
dtype=torch.float32,
)
self.register_buffer("cos", cos, persistent=False)
self.register_buffer("sin", sin, persistent=False)
def create_masks(self, seq_len, device):
ones = torch.ones((seq_len, seq_len), dtype=torch.bool, device=device)
# mask_global (future is masked: j > i)
# j: 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
# i
# 0: 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
# 1: 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1
# 2: 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1
# 3: 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1
# 4: 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1
# 5: 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1
# 6: 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1
# 7: 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
mask_global = torch.triu(ones, diagonal=1)
# far_past (too far back is masked: i - j >= sliding_window)
# where sliding_window = 4
# j: 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
# i
# 0: 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
# 1: 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
# 2: 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
# 3: 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
# 4: 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
# 5: 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0
# 6: 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0
# 7: 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0
far_past = torch.triu(ones, diagonal=self.cfg["sliding_window"]).T
# Local (sliding_window) = future OR far-past
# mask_local
# j: 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
# i
# 0: 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
# 1: 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1
# 2: 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1
# 3: 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1
# 4: 1 0 0 0 0 1 1 1
# 5: 1 1 0 0 0 0 1 1
# 6: 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 1
# 7: 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0
mask_local = mask_global | far_past
return mask_global, mask_local
def forward(self, input_ids):
b, seq_len = input_ids.shape
x = self.tok_emb(input_ids)
mask_global, mask_local = self.create_masks(seq_len, x.device)
cos = self.cos[:seq_len, :].to(x.device)
sin = self.sin[:seq_len, :].to(x.device)
for block in self.blocks:
x = block(x, mask_global, mask_local, cos, sin)
x = self.final_norm(x)
logits = self.out_head(x.to(self.cfg["dtype"]))
return logits
2. Initialize model
OLMO3_CONFIG_7B = {
"vocab_size": 100_278,
"context_length": 65_536,
"emb_dim": 4_096,
"n_heads": 32,
"n_layers": 32,
"hidden_dim": 11_008,
"head_dim": 128,
"n_kv_heads": 32,
"attention_bias": False,
"attention_dropout": 0.0,
"sliding_window": 4_096,
"layer_types": [
"sliding_attention",
"sliding_attention",
"sliding_attention",
"full_attention",
"sliding_attention",
"sliding_attention",
"sliding_attention",
"full_attention",
"sliding_attention",
"sliding_attention",
"sliding_attention",
"full_attention",
"sliding_attention",
"sliding_attention",
"sliding_attention",
"full_attention",
"sliding_attention",
"sliding_attention",
"sliding_attention",
"full_attention",
"sliding_attention",
"sliding_attention",
"sliding_attention",
"full_attention",
"sliding_attention",
"sliding_attention",
"sliding_attention",
"full_attention",
"sliding_attention",
"sliding_attention",
"sliding_attention",
"full_attention",
],
"rope_base": 500_000.0,
"rope_attention_factor": 1.2079441541679836,
"rope_type": "yarn",
"rope_factor": 8.0,
"rope_orig_max": 8_192,
"rms_norm_eps": 1e-6,
"dtype": torch.bfloat16,
"eos_token_id": 100_257,
"pad_token_id": 100_277,
}
OLMO3_CONFIG_32B = {
"vocab_size": 100_278,
"context_length": 65_536,
"emb_dim": 5_120,
"n_heads": 40,
"n_layers": 64,
"hidden_dim": 27_648,
"head_dim": 128,
"n_kv_heads": 8,
"attention_bias": False,
"attention_dropout": 0.0,
"sliding_window": 4_096,
"layer_types": [
"sliding_attention",
"sliding_attention",
"sliding_attention",
"full_attention",
"sliding_attention",
"sliding_attention",
"sliding_attention",
"full_attention",
"sliding_attention",
"sliding_attention",
"sliding_attention",
"full_attention",
"sliding_attention",
"sliding_attention",
"sliding_attention",
"full_attention",
"sliding_attention",
"sliding_attention",
"sliding_attention",
"full_attention",
"sliding_attention",
"sliding_attention",
"sliding_attention",
"full_attention",
"sliding_attention",
"sliding_attention",
"sliding_attention",
"full_attention",
"sliding_attention",
"sliding_attention",
"sliding_attention",
"full_attention",
"sliding_attention",
"sliding_attention",
"sliding_attention",
"full_attention",
"sliding_attention",
"sliding_attention",
"sliding_attention",
"full_attention",
"sliding_attention",
"sliding_attention",
"sliding_attention",
"full_attention",
"sliding_attention",
"sliding_attention",
"sliding_attention",
"full_attention",
"sliding_attention",
"sliding_attention",
"sliding_attention",
"full_attention",
"sliding_attention",
"sliding_attention",
"sliding_attention",
"full_attention",
"sliding_attention",
"sliding_attention",
"sliding_attention",
"full_attention",
],
"rope_base": 500_000.0,
"rope_attention_factor": 1.2079441541679836,
"rope_type": "yarn",
"rope_factor": 8.0,
"rope_orig_max": 8_192,
"rms_norm_eps": 1e-6,
"dtype": torch.bfloat16,
"eos_token_id": 100_257,
"pad_token_id": 100_277,
}
OLMO3_CONFIG = OLMO3_CONFIG_32B if "32B" in USE_MODEL else OLMO3_CONFIG_7B
torch.manual_seed(123) model = Olmo3Model(OLMO3_CONFIG)
model
Olmo3Model(
(tok_emb): Embedding(100278, 4096)
(blocks): ModuleList(
(0-31): 32 x TransformerBlock(
(att): GroupedQueryAttention(
(W_query): Linear(in_features=4096, out_features=4096, bias=False)
(W_key): Linear(in_features=4096, out_features=4096, bias=False)
(W_value): Linear(in_features=4096, out_features=4096, bias=False)
(out_proj): Linear(in_features=4096, out_features=4096, bias=False)
(q_norm): RMSNorm()
(k_norm): RMSNorm()
)
(ff): FeedForward(
(fc1): Linear(in_features=4096, out_features=11008, bias=False)
(fc2): Linear(in_features=4096, out_features=11008, bias=False)
(fc3): Linear(in_features=11008, out_features=4096, bias=False)
)
(post_attention_layernorm): RMSNorm()
(post_feedforward_layernorm): RMSNorm()
)
)
(final_norm): RMSNorm()
(out_head): Linear(in_features=4096, out_features=100278, bias=False)
)
– A quick check that the forward pass works before continuing:
model(torch.tensor([1, 2, 3]).unsqueeze(0))
tensor([[[ 0.3594, -0.6289, -0.2754, ..., 1.1016, 0.4219, 0.0381],
[ 1.1719, 0.0283, 0.6055, ..., 0.4863, -0.1953, 0.2246],
[ 0.4902, -0.0425, 0.6758, ..., 0.3730, -0.5781, -0.1670]]],
dtype=torch.bfloat16, grad_fn=<UnsafeViewBackward0>)
if torch.cuda.is_available():
device = torch.device("cuda")
elif torch.backends.mps.is_available():
device = torch.device("mps")
else:
device = torch.device("cpu")
model.to(device);
/home/rasbt/jupyterlab/reasoning/.venv/lib/python3.12/site-packages/torch/cuda/__init__.py:283: UserWarning: Found GPU0 NVIDIA GB10 which is of cuda capability 12.1. Minimum and Maximum cuda capability supported by this version of PyTorch is (8.0) – (12.0) warnings.warn(
4. Load pretrained weights
def load_weights_into_olmo(model, param_config, params):
def assign(left, right, tensor_name="unknown"):
if left.shape != right.shape:
raise ValueError(
f"Shape mismatch in tensor '{tensor_name}'. "
f"Left: {left.shape}, Right: {right.shape}"
)
with torch.no_grad():
if isinstance(right, torch.Tensor):
left.copy_(right)
else:
left.copy_(torch.as_tensor(right, dtype=left.dtype, device=left.device))
return left
# Token embedding
if "model.embed_tokens.weight" in params:
model.tok_emb.weight = assign(
model.tok_emb.weight,
params["model.embed_tokens.weight"],
"model.embed_tokens.weight",
)
for l in range(param_config["n_layers"]):
block = model.blocks[l]
att = block.att
# Q, K, V projections
att.W_query.weight = assign(
att.W_query.weight,
params[f"model.layers.{l}.self_attn.q_proj.weight"],
f"model.layers.{l}.self_attn.q_proj.weight",
)
att.W_key.weight = assign(
att.W_key.weight,
params[f"model.layers.{l}.self_attn.k_proj.weight"],
f"model.layers.{l}.self_attn.k_proj.weight",
)
att.W_value.weight = assign(
att.W_value.weight,
params[f"model.layers.{l}.self_attn.v_proj.weight"],
f"model.layers.{l}.self_attn.v_proj.weight",
)
# Output projection
att.out_proj.weight = assign(
att.out_proj.weight,
params[f"model.layers.{l}.self_attn.o_proj.weight"],
f"model.layers.{l}.self_attn.o_proj.weight",
)
# QK norms
att.q_norm.weight = assign(
att.q_norm.weight,
params[f"model.layers.{l}.self_attn.q_norm.weight"],
f"model.layers.{l}.self_attn.q_norm.weight",
)
att.k_norm.weight = assign(
att.k_norm.weight,
params[f"model.layers.{l}.self_attn.k_norm.weight"],
f"model.layers.{l}.self_attn.k_norm.weight",
)
# Feedforward weights
block.ff.fc1.weight = assign(
block.ff.fc1.weight,
params[f"model.layers.{l}.mlp.gate_proj.weight"],
f"model.layers.{l}.mlp.gate_proj.weight",
)
block.ff.fc2.weight = assign(
block.ff.fc2.weight,
params[f"model.layers.{l}.mlp.up_proj.weight"],
f"model.layers.{l}.mlp.up_proj.weight",
)
block.ff.fc3.weight = assign(
block.ff.fc3.weight,
params[f"model.layers.{l}.mlp.down_proj.weight"],
f"model.layers.{l}.mlp.down_proj.weight",
)
# Post-attention and post norms
block.post_attention_layernorm.weight = assign(
block.post_attention_layernorm.weight,
params[f"model.layers.{l}.post_attention_layernorm.weight"],
f"model.layers.{l}.post_attention_layernorm.weight",
)
block.post_feedforward_layernorm.weight = assign(
block.post_feedforward_layernorm.weight,
params[f"model.layers.{l}.post_feedforward_layernorm.weight"],
f"model.layers.{l}.post_feedforward_layernorm.weight",
)
# Final normalization and output head
if "model.norm.weight" in params:
model.final_norm.weight = assign(
model.final_norm.weight,
params["model.norm.weight"],
"model.norm.weight",
)
if "lm_head.weight" in params:
model.out_head.weight = assign(
model.out_head.weight,
params["lm_head.weight"],
"lm_head.weight",
)
else:
model.out_head.weight = model.tok_emb.weight
print("Model uses weight tying.")
import json
import os
from pathlib import Path
from safetensors.torch import load_file
from huggingface_hub import snapshot_download
repo_id = f"allenai/{USE_MODEL}"
local_dir = Path(repo_id).parts[-1]
repo_dir = snapshot_download(repo_id=repo_id, local_dir=local_dir)
index_path = os.path.join(repo_dir, "model.safetensors.index.json")
with open(index_path, "r") as f:
index = json.load(f)
weights_dict = {}
for filename in sorted(set(index["weight_map"].values())):
shard_path = os.path.join(repo_dir, filename)
shard = load_file(shard_path)
weights_dict.update(shard)
load_weights_into_olmo(model, OLMO3_CONFIG, weights_dict)
model.to(device)
del weights_dict
Fetching 14 files: 0%| | 0/14 [00:00<?, ?it/s]
4. Load tokenizer
from tokenizers import Tokenizer
from huggingface_hub import hf_hub_download
class OlmoTokenizer:
def __init__(self, tokenizer_file_path, eos_token_id, pad_token_id):
tok_file = Path(tokenizer_file_path)
self._tok = Tokenizer.from_file(str(tok_file))
eos_from_tok = (
self._tok.token_to_id("<|endoftext|>")
or self._tok.token_to_id("<end_of_turn>")
)
self.eos_token_id = eos_from_tok if eos_from_tok is not None else eos_token_id
pad_from_tok = (
self._tok.token_to_id("<|pad|>")
or self._tok.token_to_id("<pad>")
)
self.pad_token_id = pad_from_tok if pad_from_tok is not None else pad_token_id
def encode(self, text):
return self._tok.encode(text).ids
def decode(self, ids):
return self._tok.decode(ids, skip_special_tokens=False)
def apply_chat_template(user_text):
return (
"<|im_start|>user\n"
f"{user_text}\n"
"<|im_end|>\n"
"<|im_start|>assistant\n"
)
tokenizer_file_path = os.path.join(local_dir, "tokenizer.json")
if not os.path.exists(tokenizer_file_path):
try:
tokenizer_file_path = hf_hub_download(repo_id=repo_id, filename="tokenizer.json", local_dir=local_dir)
except Exception as e:
print(f"Warning: failed to download tokenizer.json: {e}")
tokenizer_file_path = "tokenizer.json"
tokenizer = OlmoTokenizer(
tokenizer_file_path=tokenizer_file_path,
eos_token_id=OLMO3_CONFIG["eos_token_id"],
pad_token_id=OLMO3_CONFIG["pad_token_id"],
)
prompt = apply_chat_template("Give me a short intro to large language models in 3 sentences.")
input_token_ids = tokenizer.encode(prompt)
text = tokenizer.decode(input_token_ids)
text
'<|im_start|>user\nGive me a short intro to large language models in 3 sentences.\n<|im_end|>\n<|im_start|>assistant\n'
5. Generate text
def generate_text_basic_stream(model, token_ids, max_new_tokens, eos_token_id=None):
model.eval()
with torch.no_grad():
for _ in range(max_new_tokens):
out = model(token_ids)[:, -1]
next_token = torch.argmax(out, dim=-1, keepdim=True)
if (eos_token_id is not None
and torch.all(next_token == eos_token_id)):
break
yield next_token
token_ids = torch.cat([token_ids, next_token], dim=1)
input_token_ids_tensor = torch.tensor(input_token_ids, device=device).unsqueeze(0)
if torch.cuda.is_available():
torch.cuda.reset_peak_memory_stats()
for token in generate_text_basic_stream(
model=model,
token_ids=input_token_ids_tensor,
max_new_tokens=500,
eos_token_id=tokenizer.eos_token_id
):
token_id = token.squeeze(0).tolist()
print(
tokenizer.decode(token_id),
end="",
flush=True
)
if torch.cuda.is_available():
def gpu_gb(x):
return f"{x / 1024 / 1024 / 1024:.2f} GB"
print(f"\n\nGPU memory used: {gpu_gb(torch.cuda.max_memory_allocated())}")
Sure! Here’s a brief introduction to large language models: Large models are advanced AI systems trained to process vast neural networks capable of understanding and generating human-like text, learning from vast data. They excel at many tasks across many languages and adapt to various tasks. They power modern applications widely used in NLP solutions.
GPU memory used: 13.70 GB
How we built a leading reasoning mode(olmo3)https://www.interconnects.ai/p/building-olmo-3-think
